One-stop lubrication solution | Discover the way to smoothness | Infomak

Oil Additives

TR-EPC04 Ethylene-Propylene Copolymer

TR-EPC03 Ethylene-Propylene Copolymer

TR-EPC02 Ethylene-Propylene Copolymer

TR-EPC01 Ethylene-Propylene Copolymer

Reduced Graphene Oxide Dispersions 2-5 lay Graphene Sheet Best Oil Additive

ZDDP Additive Engine Oil Additives Extreme Pressure ZDDP
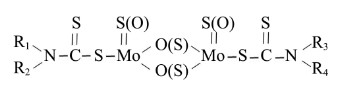
Engine Oil Additives Friction Modifier MoDTC(liquid)
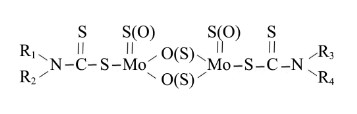
Friction Modifier Engine Oil Additives MoDTP
Overview of Oil Additives
Oil additives are chemical compounds blended right into base oils (such as petroleum-derived or artificial lubricating substances) to boost performance, appropriate shortages, or present specific residential or commercial properties that base oils alone can not give.Comprising 1-- 30% of lubricant formulas, these additives are vital in modern-day lubrication, dealing with challenges like extreme temperatures, high tons, and contamination, and put on in diverse applications, from vehicle engines to commercial machinery.

Oil additives
Features of Oil Additives
- Functionality: Reduce friction (e.g., ZDDP), inhibit corrosion/oxidation, control viscosity across temps, and disperse contaminants.
- Diverse Types: Anti-wear (AW), extreme pressure (EP), detergents, dispersants, antioxidants, and viscosity modifiers.
- Adaptability: Work in extreme conditions (high/low temps, loads) and industries (automotive, aerospace, industrial).
- Specialization: Tailored for specific needs (e.g., EV drivetrains, marine systems) with trends toward eco-friendly, multifunctional, and nano-based formulations.
Applications Across Industries
- Automotive: Engine oils utilize a blend of detergents, dispersants, and AW additives to handle stop-start cycles and high temperatures. Equipment oils depend on EP additives for durable transmissions.
- Industrial Machinery: High-temperature antioxidants and corrosion inhibitors are critical in steel mills or mining equipment, while hydraulic oils use anti-foam agents for precise fluid power control.
- Aerospace: Synthetic oils with low volatility and high thermal stability, enhanced by extreme-pressure additives for jet engine bearings.
- Marine and Offshore: Additives resistant to saltwater contamination and microbial growth, protecting propulsion systems and cargo machinery.
- Power Generation: Turbine oils with superior oxidation resistance to operate for decades in steam or gas turbines.
Production Methods of Oil Additives
- Chemical Synthesis: Key additives (e.g., ZDDP, sulfonates) are created via organic reactions like esterification, alkylation, or sulfidation, often using catalysts and controlled temperature/pressure.
- Blending/Formulation: Additives are mixed with base oils or solvents in precise ratios, using high-shear mixers or homogenizers to ensure uniformity, with heat or vacuum applied to eliminate impurities.
- Surface Modification: For nano-additives (e.g., graphene), surface treatments improve dispersion stability in oils.
- Purification: Processes like distillation, filtration, or crystallization remove byproducts or unreacted materials.
- Quality Control: Formulations are tested for viscosity, thermal stability, and performance before packaging, with adjustments made for target applications (e.g., automotive, industrial).

Company Profile
Infomak is a trusted global chemical material supplier & manufacturer with over 12-year-experience in providing super high-quality lubricant and relatives products.
The company has a professional technical department and Quality Supervision Department, a well-equipped laboratory, and equipped with advanced testing equipment and after-sales customer service center.
If you are looking for high-quality lubricant materials and relative products, please feel free to contact us or click on the needed products to send an inquiry.
Payment Methods
L/C, T/T, Western Union, Paypal, Credit Card etc.
Shipment
It could be shipped by sea, by air, or by reveal ASAP as soon as repayment receipt.
5FAQs of Oil Additives
1. What are the main functions of oil additives?
Oil additives have several important functions. They can reduce friction and wear between moving parts, improve the oil's resistance to oxidation and corrosion, control the oil's viscosity across different temperatures, keep contaminants suspended in the oil to prevent sludge formation and enhance the oil's ability to withstand extreme pressures.
2. How do I choose the right oil additive for my vehicle or equipment?
The selection of oil additive depends on several factors, consisting of the sort of engine or tools, its operating problems (such as temperature level, load, and speed), the supplier's recommendations, and the particular issues you intend to deal with.
3. Can I use too much oil additive?
The selection of oil additive relies on several elements, including the kind of engine or equipment, its operating problems (such as temperature level, lots, and rate), the manufacturer's suggestions, and the specific troubles you want to resolve.
4. Do oil additives expire?
Most oil additives have a shelf life. The expiration date can vary depending on the type of additive and its storage conditions. Generally, additives should be stored in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and heat. If an additive has expired, it may not be as effective or could cause problems when used. It's best to check the product label for the expiration date and discard any expired additives.
5. Are oil additives safe for the environment?
Lots of contemporary oil additives are developed to be much more eco-friendly. However, some older or less-regulated ingredients may have unsafe substances. When utilized effectively and according to guidelines, oil additives must not have a substantial unfavorable influence on the setting. Nonetheless, inappropriate disposal of used oil-containing additives can be harmful. It is very important to recycle made use of oil and follow local ecological guidelines to minimize any potential environmental effect.
The option of oil additive relies on several aspects, including the kind of engine or devices, its operating conditions (such as temperature, tons, and rate), the producer's recommendations, and the details problems you wish to resolve.